10 Ways Nurses Can Help Patients with Diabetes
In the world of healthcare, nurses play a pivotal role in the management and support of patients with diabetes. The condition affects millions worldwide. As the prevalence of diabetes continues to rise, the need for specialized care and patient education becomes increasingly important.
Nurses are often on the front lines of this battle, providing crucial services that range from medication management to lifestyle counseling. Their role in helping diabetic patients manage their condition is vital to both the prevention of complications and the enhancement of overall quality of life. This article explores the various ways in which nurses can contribute to the care and support of diabetic patients.
-
Educating Patients on Diabetes Management
Education is a key component in diabetes management, and nurses are ideally positioned to provide this vital information. They educate patients on how to monitor their blood sugar levels, the importance of regular check-ups, and how to recognize the signs of hypo- or hyperglycemia. Nurses also guide patients in understanding how diet, exercise, and lifestyle choices can impact their condition. By providing clear, understandable information, nurses empower patients to take an active role in managing their diabetes, which is essential for long-term health and well-being.
Education is a key component in diabetes management, and nurses are ideally positioned to provide this vital information. Share on X-
Specialized Nursing Roles in Diabetes Care
Nursing roles in diabetes care have evolved, with many nurses now specializing in this field. Nurses can pursue roles as Certified Diabetes Educators or even as specialists within hospital settings, focusing exclusively on diabetic patients. Additionally, the emergence of acute care nurse practitioner programs online has opened up opportunities for nurses to gain advanced knowledge and skills in managing complex diabetic conditions. These programs prepare nurses for roles where they can make significant impacts in acute care settings. They manage complex patient cases, and lead diabetic care teams.
-
Assisting with Medication Management
Medication management is a critical aspect of diabetes care, and nurses play a central role in this process. They assist patients with insulin administration, ensuring that the correct dosage is administered at the right times. Nurses also educate patients on the proper use of insulin pens, pumps, and syringes. For those on oral medications, nurses monitor adherence to the prescribed regimen and advise on any side effects. This oversight helps prevent complications and ensures that the medication is as effective as possible in managing the patient’s blood glucose levels.
-
Nutritional Guidance and Planning
Diet plays a significant role in the management of diabetes, and nurses often provide nutritional counseling to patients. They work with patients to develop meal plans that are both enjoyable and in line with their health needs. This might include teaching patients about carbohydrate counting, portion control, and how to read food labels effectively. Nurses also provide guidance on how to make healthier food choices that can positively impact blood sugar levels. By personalizing dietary plans, nurses help patients manage their diabetes more effectively and reduce the risk of complications.
-
Monitoring and Managing Blood Glucose Levels
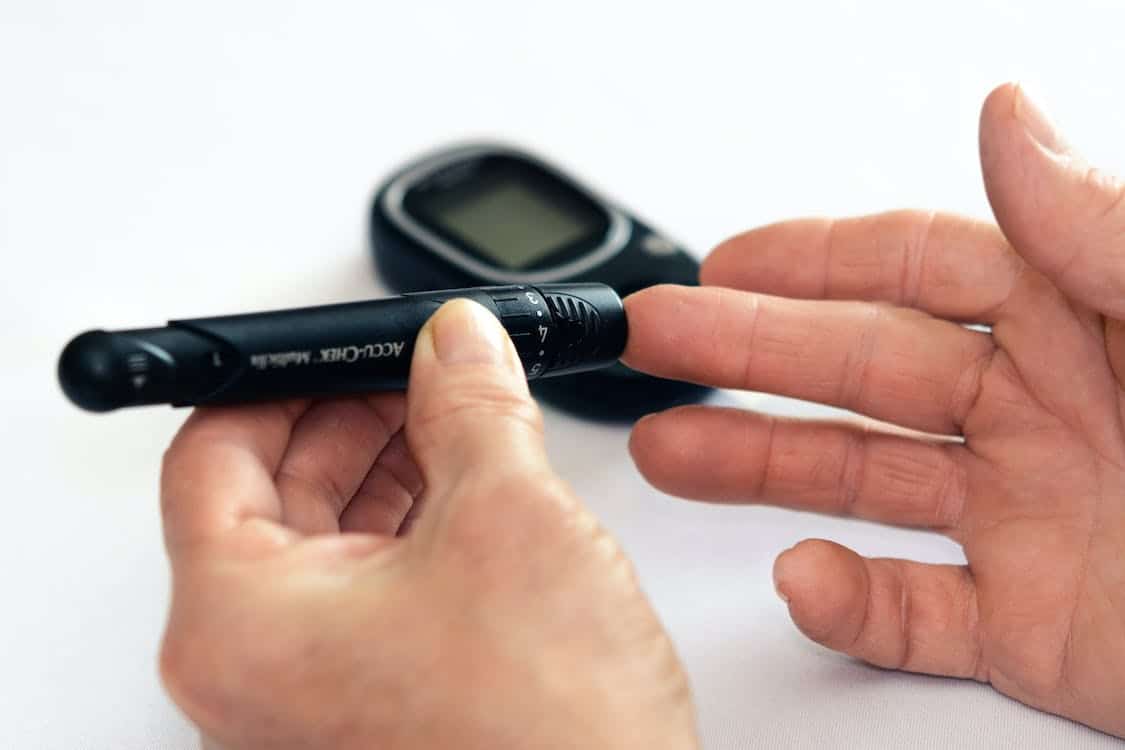
Regular monitoring of blood glucose levels is essential for diabetic patients, and nurses are instrumental in this process. They teach patients how to use glucose meters, interpret the results, and respond appropriately to different readings. In hospital settings, nurses are responsible for regular blood glucose monitoring, adjusting insulin doses as needed, and reacting swiftly to instances of hypo- or hyperglycemia. Through diligent monitoring and management, nurses help maintain stable blood glucose levels, which is critical for preventing both short-term and long-term complications associated with diabetes.
-
Wound Care for Diabetic Patients
One of the critical aspects of diabetes care that nurses handle is wound care, particularly for patients with diabetic foot ulcers. Due to the compromised healing in diabetic patients, even minor wounds can escalate into serious complications if not managed properly. Nurses are trained in the assessment and treatment of these wounds. They provide regular cleaning, dressing changes, and monitor for signs of infection. Additionally, nurses educate patients on proper foot care and the importance of early detection of foot problems. This specialized care is crucial in preventing complications that can lead to severe outcomes, such as amputation.
-
Lifestyle Modification Counseling
Lifestyle changes are fundamental in managing diabetes effectively, and nurses play a key role in counseling patients on these modifications. They work with patients to develop achievable goals for physical activity, weight management, and smoking cessation. Nurses provide support and encouragement, helping patients to understand the impact of these changes on their diabetes control and overall health. They also offer resources and strategies to overcome barriers, ensuring that patients have the support they need to make and maintain these essential lifestyle changes.
-
Emotional and Psychological Support
Managing diabetes is not only a physical challenge but also an emotional and psychological one. Nurses provide vital support in this area, offering a listening ear and compassionate care. They can identify signs of diabetes-related distress, depression, or anxiety and provide or refer patients to appropriate support services, including counseling or support groups. By addressing the emotional and psychological aspects of diabetes, nurses can help patients cope more effectively with their condition, which is essential for successful diabetes management.
-
Coordination of Multidisciplinary Care
Nurses often act as the coordinators in a multidisciplinary team approach to diabetes care. They collaborate with physicians, dietitians, podiatrists, and other healthcare professionals to develop and implement comprehensive care plans. This coordination ensures that all aspects of the patient’s health are addressed, and care is seamless. Nurses also act as advocates for their patients, ensuring that their needs and preferences are heard and respected by the broader healthcare team.
-
Advocating for Patient Needs and Rights
Advocacy is a significant part of the nursing role in diabetes care. Nurses advocate for their patients’ access to necessary healthcare services, education, and resources. They may also be involved in community advocacy, working to raise awareness about diabetes, promote healthy lifestyles, and improve access to care for diabetic patients. This advocacy is vital in ensuring that patients receive the care and support they need to manage their diabetes effectively.
Conclusion
Nurses are indispensable in the sphere of diabetes care. While offering a wide range of services that go far beyond basic medical care. From educating patients and assisting with medication management to providing emotional support and coordinating care. As a result, the nurses roles are diverse and impactful. Nurses not only contribute to the day-to-day management of diabetes but also to the long-term health and well-being of their patients. Their dedication and expertise make them crucial allies in the fight against diabetes, helping patients lead healthier and more fulfilling lives despite their condition.