Normal Blood Sugar After Eating Tips
It can feel overwhelming to keep track of your normal blood sugar after eating, especially when there’s so much conflicting information out there. In reality, your post-meal blood sugar doesn’t have to be a guessing game. A few practical steps can help you understand what’s happening in your body and keep your levels in a healthier range. About 1 in 10 Americans has diabetes (CDC), so you’re in good company if you’re looking for answers. Let’s clear up some confusion together.
Understand Normal Blood Sugar After Eating
When you eat a meal—particularly one that’s high in carbohydrates—your blood sugar naturally goes up, then settles back down as insulin (a hormone your pancreas produces) moves glucose into your cells. For people with diabetes, this process may not work as smoothly.
- Most nonpregnant adults with diabetes aim for under 180 mg/dL about one to two hours after a meal (Cleveland Clinic).
- People without diabetes generally return to normal levels (under 140 mg/dL) within two hours, although this varies.
Why These Numbers Matter
Maintaining healthy post-meal levels supports your energy, helps you stay focused, and reduces risks associated with chronic high blood sugar. If you’re consistently above target, you may develop issues like nerve damage or eye problems over time (YNHHS). By keeping your numbers in check, you’ll help prevent complications.
Tools For Post-Meal Monitoring
Tracking your post-meal blood sugar is the best way to see how your body responds to different foods. The good news? You’ve got options.
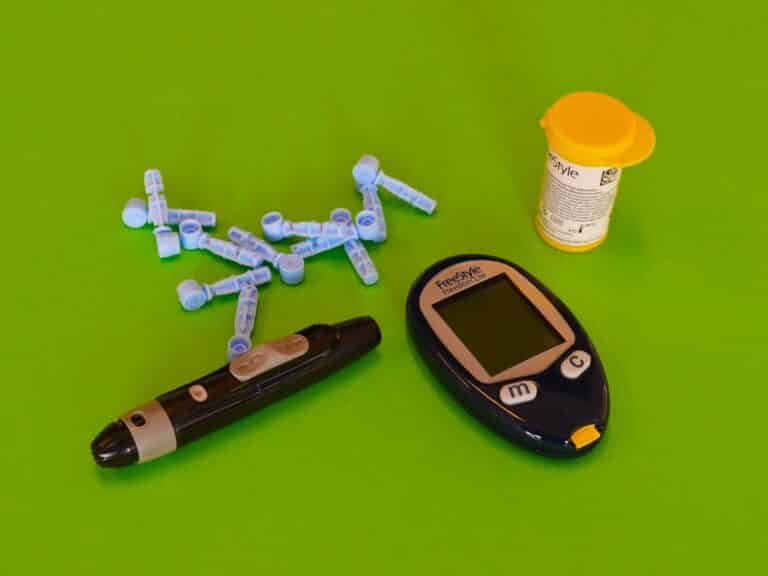
Fingerstick Or Self-Testing
A blood sugar meter is the most common option. Many are available without a prescription, although you’ll still need testing strips. You simply prick your finger, place a drop of blood on the strip, and let the meter do its thing. While not 100% accurate every time, meters offer insights you can use to adjust your meals or medication as needed (Mount Sinai).
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM)
If you want to know what’s happening 24/7, CGM systems track your glucose level throughout the day using a small sensor placed under your skin. Some systems alert you to high or low levels, which can be especially helpful. Many people still do occasional fingerstick checks to confirm CGM readings (Cleveland Clinic).
Tips To Keep Blood Sugar Steady
You don’t have to overhaul your lifestyle overnight. Consistency and small, daily steps will add up to a big difference in your post-meal numbers.
Focus On Balanced Meals
What you eat plays a key role in blood sugar fluctuations. Combine lean proteins, healthy fats, and fiber-rich carbs in your meals for a gentler impact on glucose.
Low GI Approach
Foods with a lower glycemic index (like oats, whole wheat bread, fruits, and vegetables) are digested more slowly. This gives insulin time to do its job, preventing big jumps in blood sugar (Know Diabetes UK). You can look at a diabetes food chart to discover more meal ideas that keep your numbers on an even keel.
Move After Meals
A brief walk—5 to 15 minutes—can help reduce post-meal spikes by aiding digestion and increasing insulin sensitivity (Baylor Scott & White Health). This could be as low-key as folding laundry, walking your dog, or even doing light chores around the house.
Keep A Food And Blood Sugar Log
Tracking what you eat alongside your blood sugar readings can reveal patterns you’d otherwise miss. Maybe a certain breakfast makes your numbers spike, or you notice that you handle carbs better after a short stroll. You can also compare your readings to a blood sugar levels chart and work with your healthcare provider to refine your approach.
Key Takeaways
- Aim to keep your post-meal numbers in a healthy range, around 140 to 180 mg/dL if you have diabetes, or lower if you don’t.
- Tools like blood sugar meters and CGMs can offer real-time insights into how you respond to certain foods.
- Balanced meals with lean proteins, lower-GI carbs, and enough fiber can help stabilize your levels.
- A quick walk or any light physical activity after you eat supports glucose control and boosts your overall energy.
- Logging your meals and glucose readings helps you and your healthcare team spot trends and make informed treatment decisions.
By taking these manageable steps—and working closely with your healthcare provider—you can smooth out post-meal swings and keep your blood sugar closer to your targets. It’s all about finding small, consistent habits that fit your lifestyle. Over time, you’ll discover there’s less stress around your after-meal numbers and more room for enjoying life.





Leave a Reply