Robots Are the Future of Diabetic Patient Care
According to a recent report from the Centers for Disease Control (CDC), approximately 38 million Americans have diabetes. The report further finds that rates of type 2 diabetes are surging, particularly among teens, young adults, and minorities. Still more alarmingly, the CDC has also found that 1 in 3 American adults have prediabetes. As a result, without timely intervention, they are likely to go on to develop type 2 diabetes. Researchers are finding that robots can be used in diabetic patient care with success.
Such findings have profound implications for individuals, families, and entire communities because the ramifications of a diabetes diagnosis can be severe. Whether you are diagnosed with type 1, type 2, or gestational diabetes, the potential long-term health impacts may be life-threatening. Diabetes, for instance, significantly increases patients’ risk of stroke, heart attack, renal failure, severe infections, and skin ulcerations, among other common complications.
The good news, though, is that patients and families do not have to battle this serious and chronic condition alone. Indeed, perhaps the greatest source of help for diabetic patients now comes from a pretty unexpected place. Robotics (using robots) and other tech innovations are proving instrumental in helping patients live longer and healthier lives.
Telehealth
One of the most significant innovations in healthcare in recent years may well be the advent of telehealth technologies. From health wearables enabling remote patient monitoring to virtual clinical care, telehealth is transforming the practice of medicine.
For patients with diabetes, the ascendency of telehealth in its myriad forms is proving particularly beneficial. For instance, the capacity to connect remotely with healthcare providers not only promotes consistent access to affordable, high-quality care — it also enables patients who are already medically vulnerable to avoid the potential harms of in-office care.
Patients no longer have to risk potential exposure to coronavirus or other infections. Furthermore, do those with mobility impairments have to incur the risk of falls or other injuries during transport. Rather, patients can connect with their medical team from the comfort and safety of their own homes, discussing questions and concerns and even securely transmitting photos, documents, and other relevant health data that the patient had prepared in advance of the virtual visit.
Remote Patient Monitoring
In addition, remote monitoring devices are now able to provide continuous tracking of patients’ vital signs, including blood glucose levels. These devices not only record patients’ health data across time but they can immediately alert patients, caregivers, and the patient’s medical team to concerning changes in the patient’s vitals.
This provides the peace of mind of knowing that potential medical emergencies can be quickly detected and addressed. At the same time, it enables healthcare providers to make more informed treatment decisions, decisions based on a comprehensive view of the patient’s health status, rather than on the circumscribed and often inaccurate portrait an in-office visit provides.
After all, white coat syndrome is real, and the stress of an office visit can lead to spikes in blood pressure, heart rate, and even glucose, resulting in treatments that are simply too aggressive. Telehealth, on the other hand, helps care providers to devise safer, more personalized, and more effective patient care.
Innovating Medication Delivery
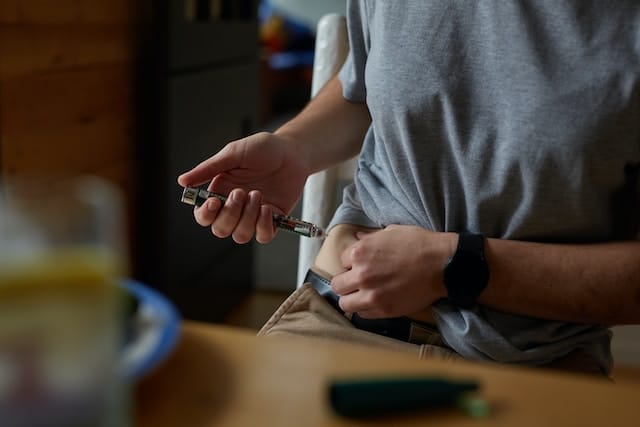
Maintaining optimal glucose levels throughout the day is a formidable challenge for every diabetic patient. However, innovations in robotic technologies (robots for diabetic patient care) are making the process far easier. Indeed, the need for patients to monitor their own glucose may soon be a thing of the past thanks to a host of new wearable and implantable devices currently under development.
For instance, automated delivery systems powered by artificial intelligence (AI).
Provide continuous monitoring of patients’ glucose levels. Many of these technologies use robotics technologies to automatically inject or release the appropriate amount of insulin when the patient needs it, relieving patients of the risk of dangerous glucose spikes or precipitous, and frightening, drops.
AI-Driven Research
Robotics and related tech innovations aren’t just transforming patient care and disease management, they’re also dramatically accelerating and enhancing medical research. For instance, AI systems are being used in medical research to analyze literally billions of data points in mere seconds. These analytics are then being transformed into new protocols both for future research and for evidence-based treatment planning.
The end result of AI-directed diabetes research is the development of new insights into disease etiology, progression, and management. Also, the formulation of new medications and care regimes. And this, ultimately, leads to better disease prevention and reduced rates of complication, morbidity, and mortality.
The Takeaway
Diabetes is a disease that is prevalent, opportunistic, and cruel. Fortunately, however, patients, families, and healthcare providers do not have to fight this adversary alone. A wide array of new technologies are emerging to aid in the war against diabetes. Diabetic patient care has successfully used these robots. From telehealth to automated medication delivery systems to research powered by artificial intelligence, robotics and related technologies are helping patients with diabetes live longer, healthier, and happier lives.