Is diabetes Contagious?
Did you know that diabetes is one of the most common chronic illnesses in the world? According to the World Health Organization, over 347 million people around the globe have diabetes. But did you also know that diabetes is not contagious, answering the Q; is diabetes transmissible? You cannot catch diabetes from another person. Despite this fact, many myths and misconceptions about diabetes are floating around. This blog post will dispel some of those myths and set the record straight. So what exactly is diabetes, and why is it not contagious? We will answer these questions and more in our detailed look at this complex disease.
Myths Debunked
You may have heard some of the following myths about diabetes. Let’s look at each one and see why it is not true.
Myth 1: Diabetes is contagious
This is perhaps the most common myth about diabetes. And it is also the most easily debunked. As we mentioned before, you cannot catch diabetes from another person. A virus or bacteria do not cause it and cannot be passed from one person to another.
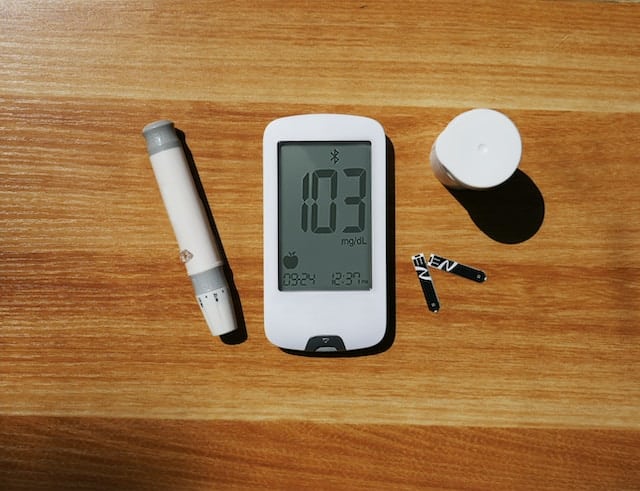
Fact #1: How do you get diabetes?
There are two types of diabetes: type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes is usually diagnosed in childhood or adolescence and is caused by the pancreas not producing enough insulin. Insulin is a hormone that helps the body to regulate blood sugar levels. Type 2 diabetes, on the other hand, develops over time and is usually diagnosed in adulthood. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or does not produce enough of it.
Fact #2: What are the symptoms of diabetes?
The most common symptoms of diabetes are increased thirst, frequent urination, and fatigue. Other symptoms include:
- Blurred vision.
- Slow-healing cuts and bruises.
- Tingling or numbness in the hands or feet.
If you experience any of these symptoms, you must see a doctor for a diagnosis.
Fact #3: Who is at risk for diabetes?
Several risk factors for type 2 diabetes include family history, age, ethnicity, and obesity. Type 1 diabetes is not as well understood, but it is thought to be caused by a combination of genetic and environmental factors.
Myth 2: Diabetes is not that serious
This myth could not be further from the truth. Diabetes is a very serious chronic illness that can lead to some complications if it is not managed properly. These complications include heart disease, stroke, kidney disease, blindness, and nerve damage. The leading cause of diabetes in the United States is kidney failure.
Myth 3: People with diabetes can’t eat sweets
While it is true that people with diabetes need to be careful about their sugar intake, they can still enjoy the occasional sweet treat. The key is to do so in moderation and to ensure that it is balanced with other foods in your meal. For example, if you have a dessert, you might want to skip the bread or starchy vegetables at that particular meal.
Myth #4: Diabetes is only a concern for people diagnosed as overweight or obese
While it is true that obesity is a major risk factor for type 2 diabetes, people of all sizes can develop the disease. One in four people with type 2 diabetes is at a healthy weight. This is because weight is not the only factor determining whether someone will develop diabetes. Other factors, such as family history and age, also play a role.
Myth #5: I don’t have to worry about diabetes because it doesn’t run in my family.
While family history is a risk factor for type 2 diabetes, it is not the only one. As we mentioned before, age, ethnicity, and obesity are also risk factors. This means that even if diabetes does not run in your family, you could still be at risk for developing the disease.
Myth #6: Diabetics must take insulin
While it is true that some people with diabetes require insulin to manage their blood sugar levels, not everyone does. People with type 1 diabetes #t1d generally require insulin. Still, people with type 2 diabetes may be able to manage their disease with other treatments, such as oral medications, lifestyle changes, and meal planning.
Myth #7: Diabetes isn’t a big deal
I can take a pill and be fine.
While diabetes can be managed with medication, it is important to remember that it is a chronic illness. This means that it requires lifelong management. People with diabetes must be diligent about taking their medication, monitoring their blood sugar levels, and making healthy lifestyle choices.
If you have been diagnosed with diabetes, it is important to see your doctor regularly and to follow their recommended treatment plan. With proper treatment, you can live a long and healthy life with diabetes.
How to support someone with diabetes
If you have a friend or family member with diabetes, you can do a few things to support them. First, educate yourself about the disease. This will help you be a better advocate for your loved one. You should also keep their treatment plan and encourage them to stick to it. Finally, offer your help in any way you can. This might mean helping them plan meals or giving them a ride to their doctor’s appointments.
If you think you or someone you know might have diabetes, it is important to see a doctor for a diagnosis. Diabetes is a serious illness, but it is manageable with proper treatment. Don’t let the myths about diabetes keep you from getting the care you need.
Final word
Diabetes is a chronic illness that requires lifelong management. There are many myths about diabetes floating around, but it is important to remember that diabetes is not contagious, and people with diabetes can still live long and healthy lives. If you think you or someone you know might have diabetes, don’t hesitate to see a doctor for a diagnosis. With proper treatment, diabetes is manageable.