Hemoglobin A1c Chart: Your Guide for Diabetes Management
Are you struggling to understand your blood sugar levels? A Hemoglobin A1c chart can be a game-changer for those looking to see where their A1C levels stand visually. This simple tool looks at your average blood glucose over the last few months, like how you’d check a report card.
Our guide explains everything from what an A1C test is to how to interpret results and even offers tips on managing diabetes efficiently. Stay healthy; read on!
Understanding the A1C Test
The A1C test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. It’s an important tool for managing diabetes and assessing the risk of complications.
What is an A1C test?
An A1C test is a blood test that shows your average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months. Doctors use it to diagnose and manage type 1 and 2 diabetes. This test determines how much glucose is stuck to the hemoglobin in your red blood cells.
This test can be obtained through a simple blood draw from a lab. It doesn’t require fasting and provides a clear picture of long-term blood sugar control.
Managing diabetes means knowing where you stand, and the A1C test gives us that crucial information.
This handy hemoglobin A1c chart helps track how well treatment plans work for people with diabetes by providing an estimated average glucose level. This way, doctors can change treatments if needed before serious complications happen.
It also alerts someone with prediabetes if they need to make lifestyle changes to avoid developing type 2 diabetes.
Why is the A1C test important?
Understanding the A1C test sets the stage for grasping its significance. This test is crucial because it helps catch diabetes or prediabetes early in people. Catching these conditions early can prevent many health problems, like heart disease, kidney failure, and nerve damage.
For those already managing diabetes, regular A1C tests guide treatment decisions and adjustments to medications. Keeping blood sugar levels within a safe range is essential to avoid complications related to diabetes.
For people with diabetes, the A1C test offers a picture of their average blood sugar control over the past two to three months. It’s more convenient than daily glucose monitoring because it doesn’t require fasting.
Testing every few years tracks how well one is keeping one’s blood sugar under control, aiming to reduce risks linked with untreated high blood sugar, such as reduced life expectancy or chronic illnesses like cardiovascular disease.
Through this testing method, individuals can monitor their progress in managing diabetes, through diet and exercise changes or medication adjustments.
When to Get an A1C Test
Get the A1C test for routine diabetes management and diagnosing type 2 or prediabetes. It’s easy to check your A1C levels and essential for staying on top of your health.
Routine diabetes management
For people with diabetes, monitoring blood sugar levels is key. This includes regular A1C tests to measure average blood glucose control over the past two to three months.
The American Diabetes Association (ADA) suggests a schedule based on your condition. If you have prediabetes, you should get tested once a year. People with type 2 diabetes who don’t use insulin need the test twice a year.
And if you have type 1 diabetes, plan for three or four tests each year.
Changes in medication or health issues might mean more tests to keep diabetes under control. Eating right and staying active play big roles, too. Medications can help manage your numbers when diet and exercise aren’t enough.
Also, tools like glucose meters and continuous glucose monitoring devices let you check your sugar levels anytime, helping avoid both high and low blood sugar complications.
Diagnosing type 2 diabetes and prediabetes
The A1C test is used to diagnose type 2 diabetes and prediabetes. An A1C level of 5.7% to 6.4% indicates prediabetes, while a 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes. For people with typical A1C results but with risk factors for diabetes, such as being overweight or having a family history of the disease, it’s advisable to get tested every three years.
A1c levels are crucial in diagnosing both type 2 diabetes and prediabetes.
How is A1C Calculated?
The A1C test calculates the average percentage of hemoglobin coated with sugar over the past 2-3 months. It’s expressed as a percentage: for example, an A1c level of 6% corresponds to an average blood glucose level of approximately 126 mg/dL over this period.
This calculation provides insight into long-term blood sugar control and helps manage diabetes.
To compute A1C, the amount of glycated hemoglobin is measured through a simple blood test. The result reflects how well your blood sugar has been controlled over time, influencing treatment decisions and diet, exercise, or medication regimen adjustments.
Understanding how A1C is calculated is crucial in effectively managing diabetes and reducing the risk of related complications.
Do I need to fast for an A1C test?
You do not need to fast for an A1C test, making it more convenient than other blood sugar tests. Fasting is unnecessary because the A1C test measures average blood sugar levels over the past 2-3 months and is unaffected by short-term changes from eating.
This means you can eat normally before taking the test, unlike some other diabetes-related tests that require fasting. Therefore, you can schedule your A1C test at any time without worrying about fasting.
Interpreting A1C Results
Understanding your A1C results provides crucial insights into your blood sugar control. Your A1C test indicates your average blood sugar levels over the past two to three months, offering a snapshot of how well you’re managing your diabetes.
Hemoglobin A1c Chart
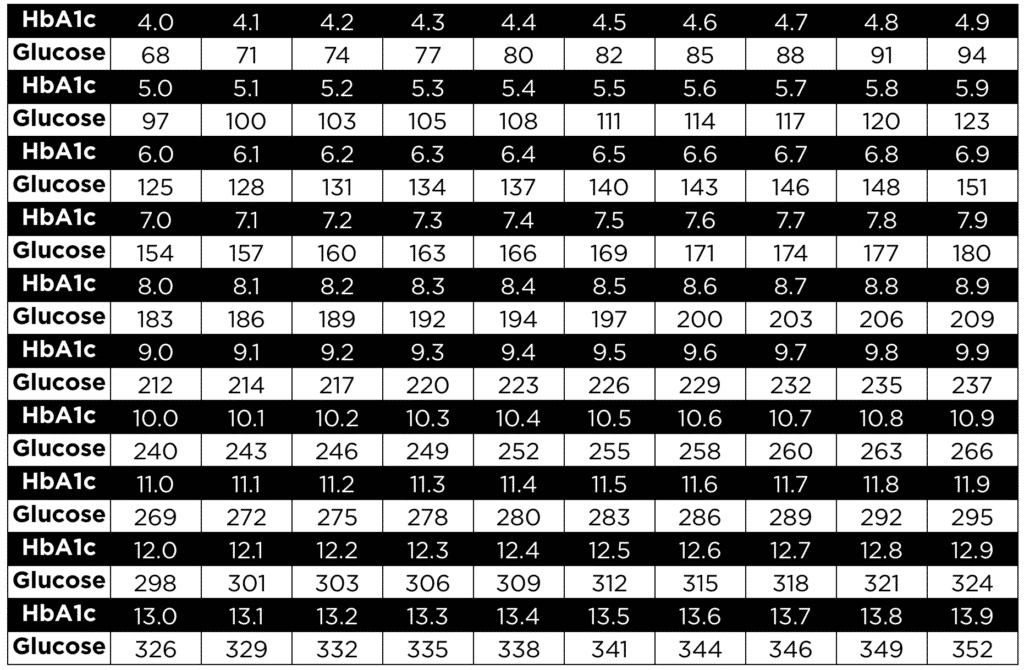
What does my A1C mean?
Your A1C level reflects your average blood sugar over the past 2-3 months. It’s stated as a percentage, with higher percentages signifying elevated blood sugar levels and greater diabetes complication risk.
- Refer to the above hemoglobin A1C chart to find your A1C percentage or average bg level.
An A1C of 5.7% – 6.4% indicates prediabetes, while 6.5% or higher indicates diabetes. For most adults with diabetes, a common treatment target is an A1c level below 7%. Higher A1c levels indicate poorer blood sugar control and an increased risk of diabetes complications.
A comprehensive understanding of what your A1C means is crucial for managing your diabetes effectively and minimizing the risk of related complications in the long run. Therefore, consistently monitoring and aiming for optimal A1C levels through lifestyle modifications, medication management if necessary, and a balanced diet focusing on carbohydrate intake regulation primarily from low glycemic index foods and regular physical activity can significantly contribute to better overall health outcomes.
What is a normal A1C?
A normal A1C range is below 5.7%, regardless of age. This level signifies reasonable blood sugar control and a lower risk of developing diabetes-related complications, such as neuropathy or chronic kidney disease.
For instance, individuals with an A1C level between 5.7% and 6.4% are considered to have prediabetes, indicating higher than normal blood sugar levels but not yet reaching the threshold for type 2 diabetes medication or treatment interventions.
What is a dangerous level of A1C?
A dangerous level of A1C generally starts at 9%. At this point, complications from diabetes could significantly rise. Monitoring and managing A1C levels are crucial to prevent adverse effects on health.
For instance, an A1C level of 6.5% or higher on two separate tests indicates diabetes, necessitating immediate attention to control blood sugar levels and prevent further complications.
Limitations of the A1C Test
The A1C test may be affected by certain factors.
It’s essential to understand the limitations of the A1C test.
Factors affecting accuracy
- Hemoglobin variants: Certain hemoglobin variants, more common in people of African, Mediterranean, or Southeast Asian descent, can lead to inaccurate A1C results.
- Medical conditions: Iron-deficiency anemia and thalassemia can influence A1C test accuracy.
- Medications and substances: Immune-suppressing drugs and high triglycerides can impact the reliability of A1C results.
- Physiological factors: Pregnancy, chronic kidney failure, cirrhosis, blood transfusions, bleeding episodes, and alcohol use disorder can lead to falsely low A1C results.
- Other influences include organ transplants and medical procedures like erythropoietin therapy, which may affect the precision of A1C tests.
A1C test vs. daily glucose monitoring
The A1C test and daily glucose monitoring are key for managing diabetes, but they serve different purposes. Here is how they compare in a simple table format.
| A1C Test | Daily Glucose Monitoring |
|---|---|
| Measures average blood sugar over 2-3 months | Shows current blood sugar level |
| No need to fast | It may require fasting for specific tests |
| Done at a doctor’s office or lab | This can be done at home with a blood glucose meter |
| Used for diagnosing diabetes and monitoring treatment | Helps with day-to-day diabetes management |
| It does not show daily fluctuations | Essential to see how food and activity affect blood sugar |
The A1C test gives a long-term view of blood sugar levels, while daily checks give instant feedback. Both are critical for good diabetes care. Keeping a close watch on daily blood sugar helps meet A1C targets. A glucose monitor at home is an excellent way to track daily levels. This tool helps make sure your A1C stays on track. This is how A1C tests and daily glucose monitoring work together in managing diabetes.
Managing A1C Levels
Lowering A1C levels involves controlling diet, exercise, and medication. Healthcare providers guide individuals in managing their A1C levels.
How to lower A1C levels
To lower A1C levels, consider the following strategies:
- Monitor your blood sugar regularly using a glucometer or continuous glucose monitoring system.
- Manage your diet by reducing intake of sugary drinks and moderating carbohydrate consumption.
- Engage in regular physical activity to help control blood sugar levels.
- Ensure proper medication adherence as prescribed by your healthcare provider.
- Aim for weight loss if overweight or obese to improve insulin sensitivity.
- Incorporate foods rich in fiber, lean proteins, and healthy fats into your diet to help stabilize blood sugar levels.
These measures collectively contribute to lowering A1C levels and promoting overall diabetes management.
The role of diet and exercise
Managing A1C levels involves crucial lifestyle adjustments. A balanced diet significantly impacts blood sugar control. Consuming fewer sugary drinks and ensuring meals are well-proportioned can help regulate glucose levels effectively.
Similarly, regular physical activity is essential for improved insulin function. Coordination between exercise, meals, and medication plays a pivotal role in managing blood sugar levels efficiently.
These measures can help individuals maintain healthy hemoglobin A1C levels by enhancing their body’s response to insulin and reducing the risk of diabetes-related complications. Therefore, a conscious effort to incorporate these dietary changes and regular exercise into daily routines becomes imperative for effectively managing A1C levels.
Medication and A1C control
Managing A1C levels includes medication as part of diabetes treatment. It’s crucial to ensure that the prescribed medications effectively control blood sugar and contribute to A1C reduction, keeping it within a healthy range.
Adjusting medications is necessary for maintaining optimal A1C levels since changes in medication can significantly impact blood glucose management. Regular monitoring supported by appropriate medication is pivotal in achieving A1C control.
A1C Test at Home
Test your A1C at home using available kits and learn how to use them accurately. Explore more about managing diabetes at home for better health outcomes.
Available home testing kits
Home testing kits for hemoglobin A1c are convenient and accessible. These kits offer rapid results in minutes, with mail-in options typically taking a few days. Rapid tests involve pricking a finger, using a collector device, and checking results after 5 minutes.
It’s important to ensure accurate usage of these home testing kits to monitor A1c levels effectively.
Moving on to “Conclusion and Next Steps”…
How to use them accurately
To use home testing kits accurately, follow these steps:
- Read the instructions carefully to understand the proper usage.
- Ensure your hands are clean before handling the testing kit to avoid contamination.
- Use the lancet provided to prick your fingertip for a blood sample, following the recommended depth.
- Apply the collected blood onto the designated test strip area per the kit’s guidelines.
- Insert the test strip into the meter and wait for the results as instructed by the manufacturer.
- Record and track your results over time to monitor your hemoglobin A1c levels changes.
By accurately following these steps, you can ensure reliable results from home hemoglobin A1c testing kits and their cost.
Conclusion and Next Steps
After understanding the A1C test and chart, managing your levels is essential. Consult a healthcare provider for regular monitoring and make lifestyle adjustments. Additionally, if you’re curious about your A1C or average blood sugar level, look at our hemoglobin A1c chart above. Finally, if you want to delve deeper into this topic, continue reading our blog for more insights and guidance.
Regular monitoring and lifestyle adjustments
Regularly monitor blood sugar levels to track changes and trends over time. Adjust lifestyle habits by incorporating regular exercise and healthy dietary choices to help manage A1C levels.
Lifestyle adjustments play a crucial role in controlling diabetes, along with regular monitoring using home testing kits to stay informed about your blood sugar status.
When to consult a healthcare provider
Consult a healthcare provider:
– For A1C levels above 9%.
– If lifestyle changes, medication adjustments, or underlying health conditions affect the frequency of A1C testing.
– When factors like alcohol use disorder, blood transfusion, chronic kidney failure, and certain health conditions may cause inaccurate A1C test results.
FAQs
What is a Hemoglobin A1c chart?
A Hemoglobin A1c chart shows the average blood sugar level over the past two to three months. It helps doctors diagnose and monitor people with diabetes by measuring glycosylated hemoglobin.
How does Hemoglobin A1c relate to blood glucose levels?
Hemoglobin A1c results are a snapshot of your average blood glucose levels, giving you an idea if your sugar levels have been too high. This test can help spot diabetes mellitus and gestational diabetes in pregnant women.
Can anyone use a Continuous Glucose Monitoring device?
Yes, people with diabetes or those experiencing symptoms like feeling tired or having low blood sugar might use CGMs along with glucometers for more detailed monitoring under their doctor’s advice.
Why is it important to keep track of HbA1c if you’re diabetic?
Keeping track of your HbA1c helps avoid complications from untreated diabetes, such as diabetic neuropathy, hyperglycemia, or even fetal macrosomia in pregnant women, by ensuring your treatment plan works well.
When should I consult a healthcare provider about my Hemoglobin A1c levels?
Consult a healthcare provider if your Hemoglobin A1c levels are higher than normal, indicating elevated blood glucose, or if you experience symptoms of hypoglycemia unawareness despite following your diabetes management plan.
Does diet affect my Hemoglobin A1c results?
Absolutely! Foods high in carbohydrates can impact your hemoglobin A1C chart readings, leading to changes in estimated average glucose (EAG). Managing what you eat, alongside taking any prescribed diabetes medications, plays a crucial role in controlling your condition.