Managing Your Diabetes and Maintaining a Healthy Lifestyle Tips
Diabetes is a serious disease that affects millions of Americans, including children, teens and adults. Although there is no cure for diabetes, it can be managed through diet, exercise and medication. It’s important to manage diabetes so you can prevent complications such as kidney disease, heart disease and blindness. We’ve put together some tips on how you can manage your condition at home!
Exercise
One of the most important aspects of managing diabetes is exercise. It can help you control blood sugar levels and lose weight, which are both key factors in preventing complications from developing. Many skin specialists encourage exercise in your daily life as it enhances the skin quality as well. Exercise also has many other benefits that make it worth doing:
- It helps you sleep better at night, which makes it easier to wake up in the morning and get going on your day.
- It gives you more energy throughout the day so that even when things get stressful or busy, you’ll still be able to keep going strong until everything settles down again (and then maybe even after).
- Exercise makes us feel good about ourselves because we know we’re taking care of ourselves–and sometimes this feeling lasts long after our workout ends!
Eat a balanced diet including fruits, vegetables and whole grains
The diet you eat is very important in managing your diabetes. A balanced diet will help you feel better, think more clearly, and prevent or delay complications of the disease. It’s also important for people with diabetes to eat a variety of foods from all the food groups: fruits and vegetables; grains (breads and cereals); milk products; meat and beans; fats and oils; sweets/desserts (candy). Intake of whey protein is also effective in diabetes.
- Eat fruits (fresh or frozen) with every meal
- Eat vegetables at least 3 times each day
- Choose whole grains over refined ones whenever possible (e.g., white bread vs whole wheat bread)
Manage stress
Stress is another factor that can make your diabetes worse. Stress can cause you to eat more, which leads to weight gain and increased blood sugar levels. It also makes it harder for you to sleep, which can affect your overall health and well-being. Stress can even make exercising difficult because it’s hard for people who are under stress to focus on the task at hand when their mind is preoccupied with other worries or concerns.
To help manage stress levels:
- Take time out in the day just for yourself–a walk around the block, reading a book or watching TV without any distractions will help clear your mind so that when it’s time for bedtime, you’ll be able help yourself relax enough so that sleep comes easier than usual (and this means better quality sleep).
- Practice relaxation techniques such as deep breathing exercises before bedtime so they become routine habits instead of something else new added into an already busy schedule; over time these rituals will become automatic responses without having too much effort put into them at first glance
Quit smoking
Smoking is bad for your health. It can cause diabetes, heart disease and stroke, cancer and erectile dysfunction. If you smoke, quitting will help you to manage your diabetes better by reducing the risk of complications from the disease.
You should also avoid drinking too much alcohol because of its effects on blood glucose levels. Alcohol can make it harder for people with type 2 diabetes who take insulin or tablets (such as sulphonylureas) to control their condition effectively if they drink more than two units per day on a regular basis (1 unit = 8g alcohol). Drinking may also increase blood pressure in people who already have high blood pressure
Get tested for diabetes
If you’re not sure whether or not you have diabetes, there’s a simple test that can tell. The American Diabetes Association recommends that everyone between the ages of 18 and 70 get tested for diabetes at least once every three years. If you are over 30 years old and overweight (with a body mass index of 25 kg/m2 or higher), that recommendation increases to annually.
Your doctor might think it’s necessary to send blood samples to be analyzed by a lab technician. If the results show high levels of sugar in the blood–that is, if they show that someone has either prediabetes or full-blown type 2 diabetes–your physician will recommend lifestyle changes and medication as part of treatment plans tailored specifically for each person based on her needs.
Eat Breakfast
Breakfast is the most important meal of the day, and it can help you manage your diabetes. A healthy breakfast will provide you with energy to get through the morning and keep your blood sugar levels from spiking. A good example of a healthy breakfast would be whole grains, fruits, vegetables and low-fat dairy or meat products such as eggs or yogurt with fruit on top.
Whole grains are rich in fiber which helps control blood sugar levels by slowing down their absorption into your bloodstream after eating them so they don’t cause spikes in glucose levels like refined carbohydrates do (like white breads).
Fruits and vegetables also provide nutrients that may lower risk factors associated with developing type 2 diabetes; these include antioxidants found in berries as well as magnesium found in spinach which reduces insulin resistance while lowering blood pressure! Plus they’re delicious!
Eating breakfast every day can also help curb hunger between meals so that snacking doesn’t become an issue later on down throughout day either – especially when traveling around town running errands all day long without any breaks between meals due time constraints or transportation issues etcetera..
Exercise Regularly
Exercise is a great way to manage your diabetes and improve your overall health. It can:
- Help you lose weight, which can lower blood sugar levels.
- Boost energy levels and make you feel more energetic overall.
- Help you sleep better at night, because exercise improves sleep quality for many people with diabetes who have sleep problems (1).
The benefits of exercise go beyond just physical health; research shows that regular physical activity also reduces depression symptoms in people with type 2 diabetes (2), lowers blood pressure (3), decreases risk for heart disease (4) and stroke (5), improves memory function in older adults with mild cognitive impairment or dementia due to type 2 diabetes (6), reduces insulin resistance in obese youth with high triglyceride levels (7), improves cholesterol levels in overweight middle-aged women who are not trying to lose weight(8), lowers their risk of developing Type 2 Diabetes mellitus over time by reducing visceral fat mass while increasing lean body mass
Check Your Blood Sugar at Least Once a Day
Checking your blood sugar at least once a day is the best way to ensure that you are keeping it within the healthy range. It is important to check before breakfast, after meals and at bedtime. You should also check when you feel sick or have a bad headache, as well as when you feel tired or have trouble sleeping.
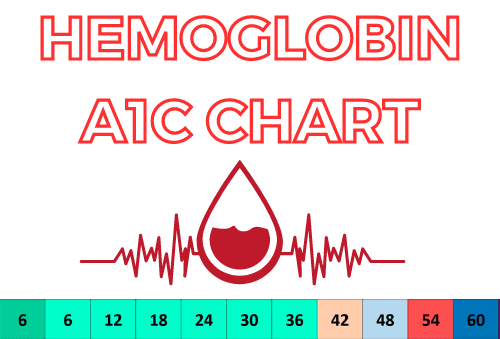
Know Your Numbers
Knowing your blood sugar level is important to managing diabetes. If your doctor has prescribed medication for you, he or she will also give instructions on how often to check your blood sugar levels.
If you are using insulin injections, it is recommended that you check your blood sugar at least two times a day (once before breakfast and once around bedtime).
It’s important to know what a normal range of blood sugar should be because this can help determine if something needs attention or not. A normal range for non-diabetic people is between 70 mg/dl (milligrams per deciliter) and 100 mg/dl before meals; after meals it should be less than 180 mg/dl; while sleeping it should be less than 120 mg/dl but not lower than 60 mg/dl within an hour after waking up in the morning
Make Healthy Food Choices
- Eat smaller portions of healthy food.
- Avoid sugary drinks and foods that are high in fat.
- Eat more fish and less red meat, as well as other sources of protein such as beans and nuts.
- Limit your intake of high-fat dairy products like butter, cheese, cream and ice cream.
Get Regular Eye Care for Diabetics
If you have diabetes, it’s important to get regular eye exams. Diabetes can cause damage to your eyes and lead to vision issues such as cataracts and glaucoma. Cataracts are clouding of the lens of your eye; they’re common in people with diabetes because of high blood sugar levels over time. Glaucoma is an increase in intraocular pressure (pressure within the eyeball), which may cause damage or loss of vision if left untreated.
Use Diabetes Medications According to Doctor’s Instructions
Diabetes medications are a key part of the treatment plan for diabetes. They can be used to lower blood sugar levels and prevent complications from developing.
However, it’s important to understand that these medications come with risks and side effects. If you have been prescribed a medication for your type 2 diabetes, make sure that you take it according to doctor’s instructions (for example: how often), or else you could risk experiencing negative effects on your health.
If at any point during treatment with these drugs do not feel well or notice any changes in how well they are working for you, contact your doctor immediately so that adjustments can be made accordingly!
Be Aware of Diabetes Complications and Other Health Risks
Diabetes complications, such as heart disease and stroke, are some of the leading causes of death for people with diabetes. The risk of experiencing one or more complications increases as your blood sugar levels rise over time.
- High blood pressure (hypertension)
- Heart disease
- Stroke
If you have diabetes, it’s important to take steps to prevent these serious health issues from happening. You can do this by keeping tabs on how well you’re managing your condition through regular checkups with your healthcare provider and following their recommendations for treatment plans that fit into your lifestyle while also addressing any other health issues that could be contributing to poor blood sugar control.
It is important to manage diabetes to prevent serious complications such as kidney disease, heart disease, blindness and amputation.
It is important to manage diabetes to prevent serious complications such as kidney disease, heart disease, blindness and amputation. Diabetes can affect the eyes, kidneys, heart and blood vessels. People with diabetes have a higher risk of developing these complications than those without the condition.
It is also important that you know about these common signs of complications:
- Blurry vision or changes in how your eyes feel (for example burning) can be an early sign of diabetic retinopathy
- Feeling tired or weak may mean your blood sugar levels aren’t under control
The best way to manage diabetes is to live a healthy lifestyle
The best way to manage diabetes is to live a healthy lifestyle. Eat a balanced diet, exercise regularly and manage stress. Don’t smoke or use other tobacco products. Get tested for diabetes if you are over 45 years old or have any of these risk factors:
- A family history of diabetes
- Obesity (BMI greater than 30)
- High blood pressure (140/90 mm Hg) or on medication for high blood pressure
If you have been diagnosed with prediabetes or insulin resistance: Make changes in your eating habits and start an exercise program that includes strength training at least three times per week for about 30 minutes each session; get screened for high blood pressure every year; stop using tobacco products; monitor your blood pressure regularly with home monitoring devices if prescribed by a doctor since there is no evidence that self-monitoring can improve health outcomes compared with routine office visits where measurements are taken by trained staff in medical centers.
Conclusion
If you have diabetes, it’s extremely important to manage your condition and lead a healthy lifestyle. The helpful tips in this article will guide you in the right direction.
Image Credit