Key Diabetes Management Metric: A1c Levels
A1c, or glycated hemoglobin, is an important diabetes measure. This test gives a complete picture of a person’s two—to three-month average blood sugar levels. Healthcare practitioners and diabetics must understand A1c readings to evaluate diabetes management options.
What Does an A1c Test Measure?
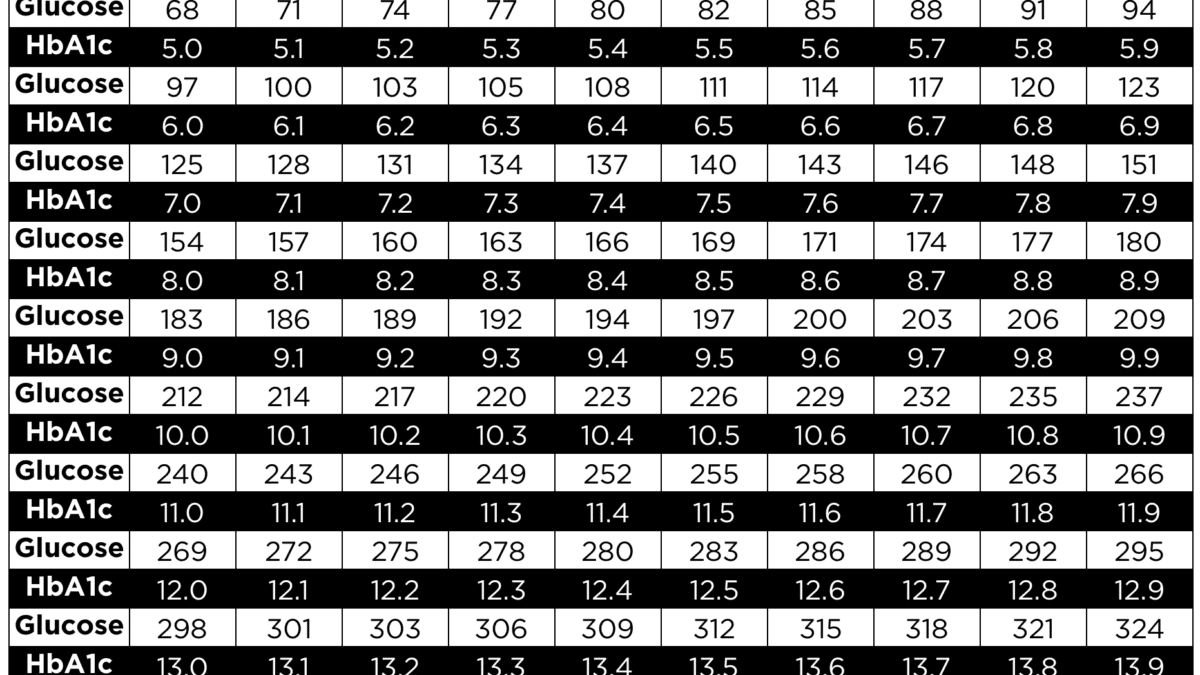
The A1c test measures the percentage of red blood cells that have glucose-coated hemoglobin. More glucose binds to hemoglobin during prolonged high blood sugar. The A1c test quantifies this proportion, indicating average blood sugar levels throughout time. Daily glucose monitoring shows short-term swings, but A1c shows longer-term trends.
The A1c Interpretation
The typical range for A1c is below 5.7%; A1c readings between 5.7% and 6.4% indicate prediabetes, whereas 6.5% indicates diabetes. Higher A1c levels increase diabetic complications! A1c levels that stay high can cause cardiovascular disease, renal damage, and nerve damage.
Important in Diabetes Management
Diabetes patients prioritize A1c management. Lifestyle changes, medication, and insulin therapy are evaluated regularly. Target A1c values depend on age, health, and comorbidities. Clinicians and patients create individualized A1c targets and develop methods to meet them, such as treating every day as a new day to fight diabetes.
Improving A1c
Numerous lifestyle changes improve A1c management! These include eating a balanced diet with fiber, fruits, and vegetables, exercising regularly, and keeping a healthy weight. Oral antidiabetic medications and insulin can help control blood sugar. Diabetes care requires blood glucose self-monitoring and treatment plan changes, like juggling balls in the air.
Issues and Considerations
A1c has limits despite its value. A1c levels are affected by age, race, and medical problems. The test may also misrepresent short-term blood sugar fluctuations. Thus, healthcare providers may employ complementing metrics like CGM to explain blood sugar changes better.
Conclusion
A1c values are significant in the fight against diabetes. Understanding the importance of this test encourages diabetics to engage in their care and drives healthcare professionals to adapt therapies. A1c monitoring helps diabetics control blood sugar and lower the risk of long-term problems.