Importance of Blood Sugar Management in Diabetes
Diabetes is a chronic condition that must be managed responsibly. The good news is that modern medicine understands more about this condition than at any time in the past. Medications, diet planning, and a number of other resources make it possible to structure a viable plan for blood sugar management and enjoy a high quality of life.
Why does the management of your glucose levels matter? Here’s some basic information that will help illustrate the point. Remember that you should always consult with your doctor to ensure that those management efforts are working.
Understanding What Constitutes Healthy Blood Sugar Levels
What is considered an acceptable range for the average blood sugar levels? Many health professionals hold that 72 to 99 mg/dL (4.0 to 5.4 mmol/L) is considered a healthy range for what’s known as fasting blood sugar levels. After consuming a meal, your blood glucose reading within two hours should be 140 mg/dL (7.8 mmol/L) or less (ADA).
Consequences of Poor Management in Type 2 Diabetics
People with this form of diabetes do produce some insulin. There’s just not enough to prevent unhealthy sugar spikes. With the aid of oral medications or injections coupled with a customized diet plan, it’s easier to keep your levels within a safe range.
What can happen if you’re not in control of your type 2 diabetes? The immediate effects of hyperglycemia (high blood sugar) include difficulty thinking, loss of energy, and lethargy. Some type 2 diabetics also notice that they urinate more often and experience greater thirst.
In the long term, blood sugar levels that remain consistently elevated are likely to result in a partial or complete loss of vision, cardiovascular issues, and problems with the kidneys. There’s also a loss of sensation in the extremities and the potential for losing toes, feet, or limbs.
What Happens When Type 1 Diabetes is Not Managed Properly?
Type 1 diabetics produce little to no insulin. Injections supply the body with what it needs to process carbohydrates properly. With this form of diabetes, the focus is not just about avoiding levels that are too high; the type 1 diabetic must also be concerned about hypoglycemia (low blood sugar.)
When blood sugar levels drop below a safe level, the individual is likely to feel jittery and unable to focus. Anxiety is not uncommon. The heartbeat may become irregular and dizziness can develop. In the most severe cases, the individual is unable to move or speak until the blood sugar level is restored to an acceptable range.
Over time, many of the same health issues that type 2 diabetics experience may also develop in type 1 diabetics. That includes loss of sensation, vision problems, and heart issues.
Day to Day Management of Blood Glucose
Plan meals that are rich in nutrients but include lower amounts of carbohydrates. Using the glycemic index will help you identify food and beverage choices that provide more nutrition and fewer carbohydrates. Keep the amount of carbs consumed per meal in line with the guidelines provided by your doctor.
Exercise helps keep the body stronger and promote the conversion of blood sugar into energy. Shoot for some form of exercise daily, even if it’s no more than a brisk 30-minute walk after the evening meal.
Taking your medication on time is essential. Some diabetes medications should be taken with meals. Others should be taken 30 minutes to an hour before eating. Following the instructions that come with the medications makes it easier to enjoy the best blood sugar management results.
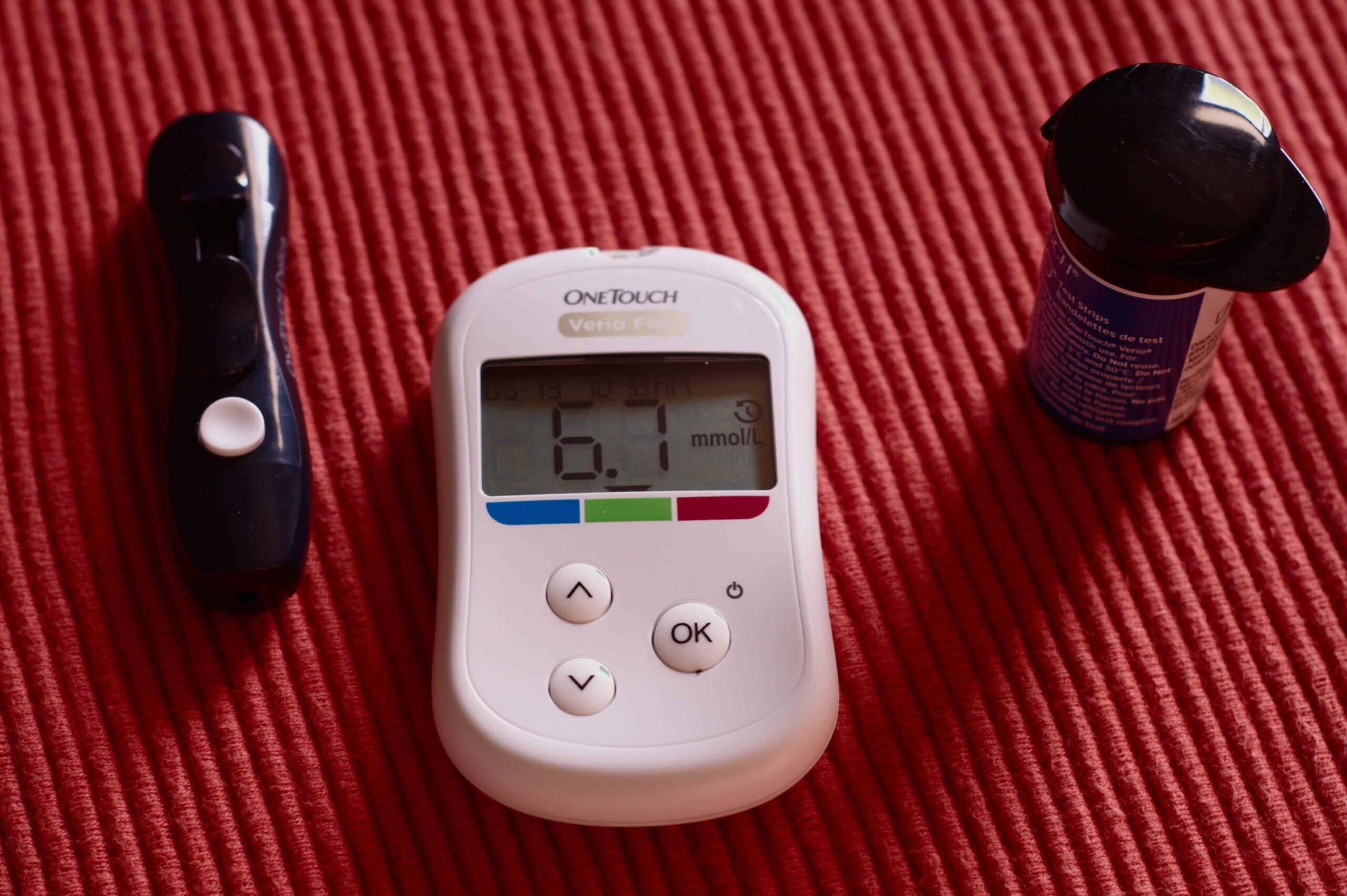
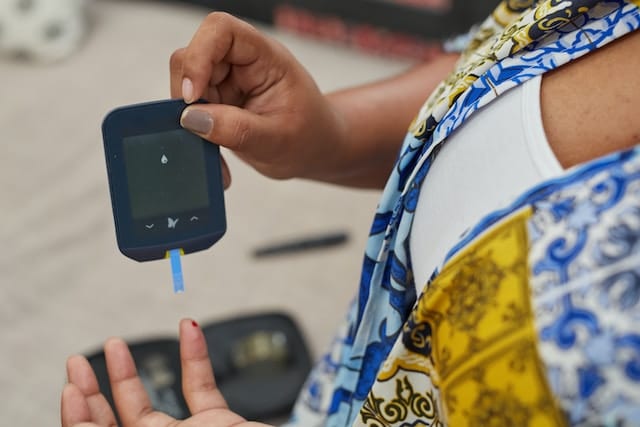
Finally, test your blood sugar levels at least once daily. Testing when you wake up and two hours after meals is not too much. That information will help you get a better handle on how your body responds to certain foods and make the meal planning process easier.
Testing and Your Doctor
Along with what you do at home, see your doctor on a regular basis. Expect the doctor to collect blood samples to determine how well your efforts are paying off. One of the more important things the doctor will do is order what’s known as an A1C test.
This test measures the amount of hemoglobin A1C found in your blood. For diabetics, the goal is to find a concentration that’s 7% or less. If your reading is closer to 6%, then your management plan is working. If not, it may be time to change your diet, exercise plan, or talk about changes to the medication. You can try our A1c calculator tool to calculate your average blood glucose level.
Conclusion
It’s possible to live a long and happy life even if you have some form of diabetes. Educate yourself, use proper blood sugar management methods, change the way you eat, work out, and live in general. See your doctor regularly and take the medication needed to manage your levels and minimize illness. In the best-case scenario, you will live to a ripe old age with few if any complications.