Everything You Need To Know About Insulin Shots
Insulin is a medication that’s used mostly for people with Type 1 diabetes, although those with Type 2 and gestational diabetes may also need it if other methods don’t help them. It’s an important tool to keep you healthy, and is usually delivered into the body via shot. Here’s everything you need to know about insulin shots before you start taking them.
The Importance Of Insulin
Your body usually creates insulin via the pancreas. It’s needed to allow the usage of glucose, which creates energy. Glucose is created when the body breaks down the carbohydrates in the things you eat. It gets used for energy, and any excess is stored in the liver. That stored glucose will only be released if you need extra energy, or when you’re stressed.
For those that have diabetes, they’ll have an inability to properly produce insulin. There are two different types of diabetes:
- Type 1: This is an autoimmune disease, leading the cells in the body to attack themselves. The body has destroyed the insulin producing cells in the pancreas, and so the patient will need insulin shots to give the body what it needs. Type 1 diabetes ( #T1D ) is most commonly seen in young people, although adults can get it too.
- Type 2: In these cases, diabetes comes about due to health, weight and exercise issues. Doctors find these patients have a resistance to insulin, high blood sugar, and a relative lack of insulin. Anyone with Type 2 diabetes ( #t2d ) is at risk of heart disease, stroke, kidney failures, and other illnesses. Learn more about managing t2d.
Diabetes Treatments Through Shots
People with either type of diabetes can find treatment through insulin shots. Type 1 patients use it to control their blood sugar level, while Type 2 patients will use it if changes in diet and exercise aren’t enough to control their levels.’
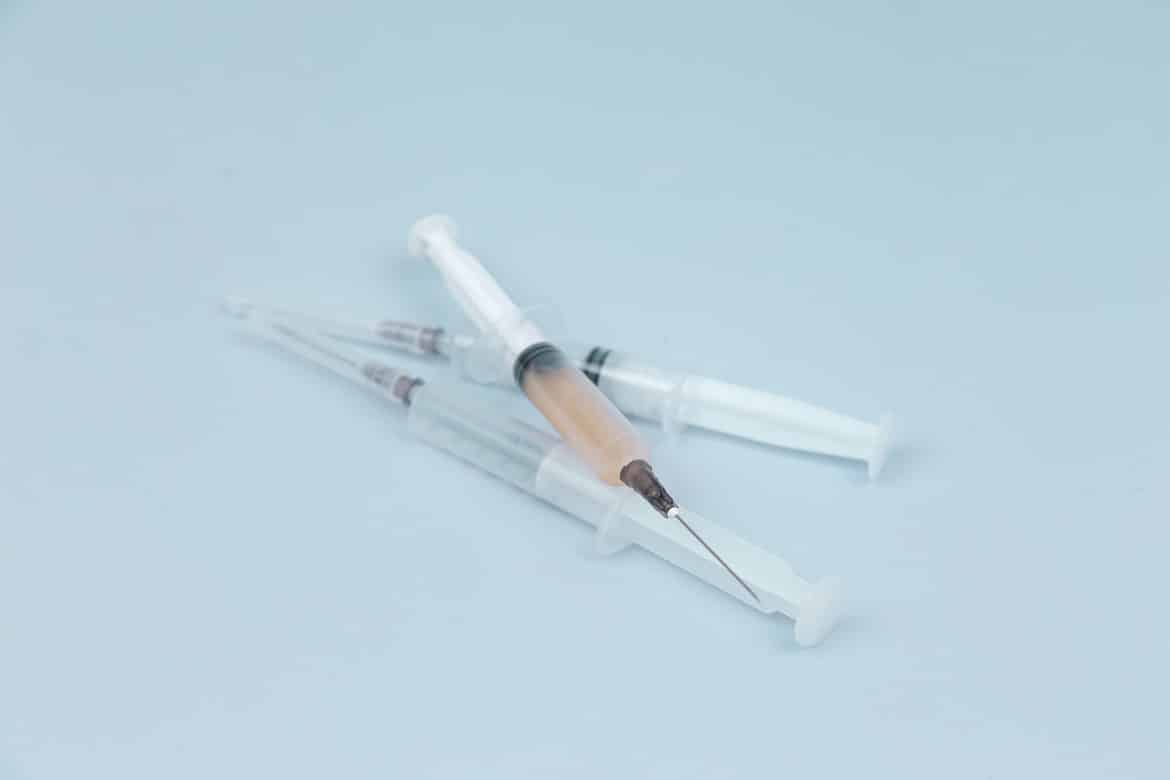
There are several different types of insulin shots, and the one you use as a diabetes patient will depend on your own needs.
- Rapid acting insulin: Once administered, this should start working within 15 minutes. It’s usually taken before a meal, and should last for 3 to 4 hours.
- Short acting insulin: This will be administered an hour before a meal. It starts working after 50 minutes, and will last anywhere from 5 to 8 hours.
- Intermediate acting insulin: As the name implies, this shot will start working 1 to 2 hours after injection, and lasts for 14 to 16 hours.
- Long acting insulin: This shot starts working after 2 hours, and can last up to 24 hours.
The shot that’s best for you will be different from person to person. When you’re deciding on treatment with your doctor, they’ll help you decide on the right kind of shot for you.
How To Administer Insulin Shots
The exact way you administer your shots will depend on your needs, and your doctor will go through all the details with you. Usually though, you’ll be required to inject it under the skin on your thighs, buttocks, upper arms and abdomen. ‘If injecting into the abdomen, you must ensure you’re more than two inches away from your belly button. If you do so, then your body won’t be able to absorb the insulin properly.
Shots are needed for insulin, as the treatment doesn’t work when taken orally. The exact amount you take, and how often you take it, will be decided between you and your doctor.
Insulin Reactions And How To Manage Them
If you are exercising too much and not getting enough calories, you could have an insulin reaction. This can show as tiredness, inability to speak, sweating, confusion, and loss of consciousness. If you have any of these symptoms, eat or drink a fast-acting carbohydrate. This can be ½ a cup of fruit juice, or 2 tablespoons of raisins. Blood sugar management is key!
Now you have an overview of insulin shots and how they work. When you work together with your doctor, you’ll be able to manage the symptoms of your diabetes with ease. Work with them to get the right dosage and frequency, and you’ll see the effects on your health.
Article by Kendra Beckley – AWS