How to Reduce the Effects of Diabetes
Diabetes is a life-threatening illness. Adhering to your diabetes treatment plan requires 24-hour dedication. However, your efforts are commendable. Consistent diabetes management may help you avoid major — even life-threatening — complications. Here are some strategies for being more involved in your diabetes management and ensuring a healthy future. Learn about how to reduce the effects of diabetes.
1. Maintain Healthy Blood Pressure and Cholesterol Level
As with diabetes, hypertension may cause damage to your blood vessels. High cholesterol is also a cause for worry since the accompanying damage is often more severe and quick when diabetes. When these diseases occur concurrently, they may result in a heart attack, stroke, or other potentially fatal conditions. You may use readily accessible remedies such as hemp pods to help you keep the proper bodily state.
Consuming a nutritious, low-fat, low-salt diet, abstaining from excessive drinking, and exercising may help manage high blood pressure and cholesterol. If required, your health care professional may also suggest prescription medicine.
2. Make a Commitment to Diabetes Management
Members of your diabetes care team — for example, your primary care physician, a diabetes care and education expert, and a dietician — can assist you in learning the fundamentals of diabetes care and give ongoing support. However, it is entirely up to you to manage your illness, and reduce your diabetes effects.
Acquire as much knowledge as possible on diabetes. Make a point of including a healthy diet and physical exercise in your everyday routine. Keep a healthy weight.
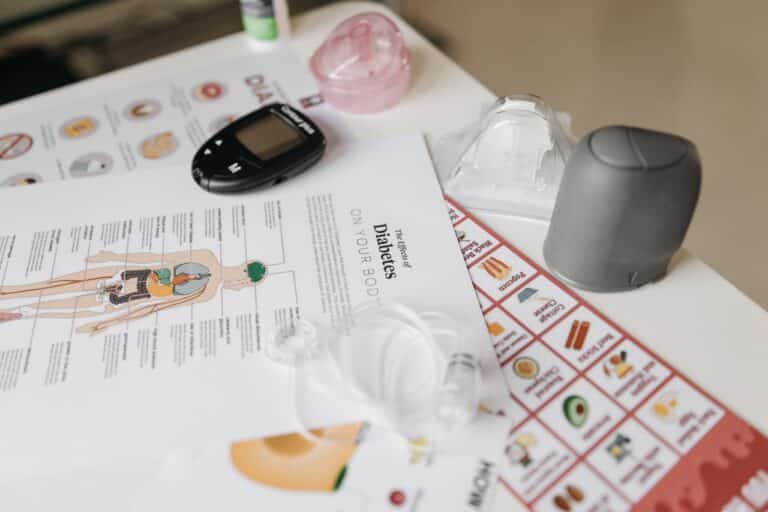
Monitor your blood sugar levels and adhere to your health care provider’s directions for blood sugar management. As advised by your health care practitioner, take your prescriptions. When you need assistance, contact your diabetes treatment team.
Excessive or insufficient sleep might boost your hunger and desire for high-carbohydrate meals. This may result in weight gain, which increases the chance of developing issues such as heart disease. Therefore, seven to eight hours of sleep every night is the goal. If you have sleep apnea, addressing it might help you sleep better and maintain a healthy blood sugar level.
3. Make Routine Physical Examinations and Eye Exams a Priority
In addition to your annual physical and normal eye examinations, schedule two to four diabetes checks every year.
During the physical, your health care provider will inquire about your diet and exercise level and will check for diabetes-related issues — such as kidney damage, nerve damage, and heart disease — as well as other medical concerns. Additionally, they will inspect your feet for any potential problems that need treatment.
Your eye care professional will examine your eyes for indications of retinal degeneration, cataracts, and glaucoma.
Stress might cause your blood glucose levels to increase if you have diabetes. Eliminate any physical or mental pressures that you can. Develop coping mechanisms for dealing with people. If you have type 2 diabetes, relaxation practices such as breathing exercises, yoga, and meditation may be extremely beneficial.
4. Diet
Reduce your salt intake. It may help you maintain a healthy blood pressure level and preserve your kidneys. Not salting your meals may not be sufficient. The majority of salt consumed by Americans comes from processed foods. Avoid convenience meals and, if possible, use fresh ingredients. When cooking, season using herbs and spices rather than salt.

Adults 51 years and older and those with high blood pressure, diabetes, or chronic renal disease should see their physician about how much salt to cut. In general, individuals with diabetes should limit their carbohydrate intake to fewer than 2,300 mg per day, although your doctor may prescribe a lower quantity.
Alcohol may result in either high or low blood sugar levels, depending on how much you drink and if you consume food concurrently. If you prefer to consume alcohol, do it in moderation, defined as no more than one drink per day for women and two drinks per day for males.
Always consume alcohol with a meal or snack, and keep in mind that the calories from alcohol are included in your daily calorie total. Additionally, be aware that alcohol may result in subsequent hypoglycemia, particularly dangerous for persons who take insulin.
When you live with diabetes, it’s natural to feel overwhelmed, unhappy, or furious. You may be aware of the measures you should take to maintain your health but have difficulty keeping to your strategy over time. This section contains information on how to manage your diabetes, eat healthfully, and stay active. We hope you found this article informative for reducing your diabetes effects.
Image Credit