Type 1 Diabetes Knowledge and Treatment Options
Two most common types of diabetes are type 1 and type 2. Type 1 diabetes, aka insulin-dependent diabetes, is a disease of the lean and young. A majority of type 1 diabetes diagnoses occur before the end of adolescence. This means that it has to be managed lifelong with the correct information of type 1 diabetes knowledge.
It frequently starts abruptly, may present itself as flu-like symptoms, along with nausea, polyuria (frequent urination), polydipsia – unusual thirst. In some cases, complications may occur in the very beginning due to extremely high levels of blood glucose or sugar.
What is type 1 diabetes?
The prevalence of type 1 diabetes is equal in various social groups; the risk of developing it are similar in rural and urban areas. Fortunately, it’s less common than type 2 diabetes. Less than 10% of all cases of diabetes are type 1.
Type 1 diabetes differs significantly from type 2, so with adequate diabetes knowledge, you can readily differentiate the two. T1D is an autoimmune disease. Meaning, in type 1 diabetes, the immune system starts attacking and killing insulin-producing beta cells in the pancreas. Thus, in type 1 there is absolute insulin deficiency unlike type 2 diabetes, which develops gradually due to ensuing insulin resistance.
Although we know that in type 1 diabetes, our immune system kills insulin-producing beta cells, we don’t know why. It is thought to occur due to a combination of reasons, like genetics and viral infections. Also the presence of other autoimmune conditions, changes in gut bacteria, and so on.
Interestingly, type 1 diabetes may not start abruptly in all cases. Some may have so-called prolonged honeymoon periods with relatively normal blood glucose levels. Nonetheless, such remissions are short-lived before full-blown diabetes follows.
Clinical symptoms of diabetes
In most cases, an experienced physician will be able to confirm the diagnosis based on clinical symptoms, type 1 diabetes knowledge, and by carrying out a blood glucose test. Frequently, a doctor may order more than one kind of blood glucose test to confirm diabetes.
Generally, the age of onset, the abruptness of disease and its symptoms are enough to say that diabetes is of type 1. However, in a small number of cases physician may order some more specific tests. These tests include C-peptide, insulin autoantibodies, islet cell cytoplasmic autoantibodies, and so on. Such an analysis may confirm the type of diabetes.
Treatment options in type 1 diabetes
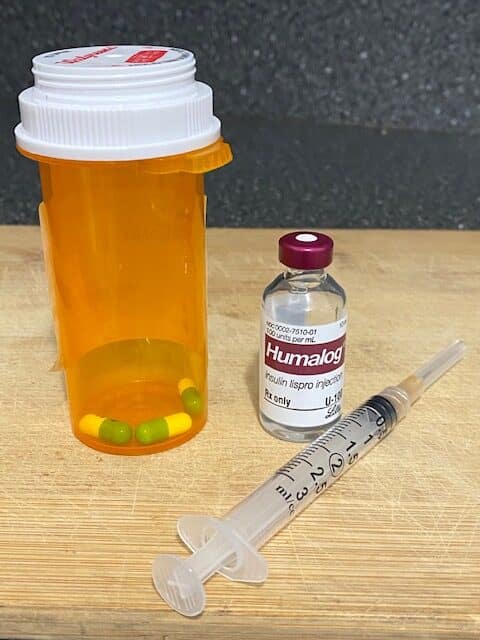
Since in type 1 diabetes there is absolute insulin deficiency due to the destruction of beta cells, insulin therapy remains the primary treatment. In type 1 diabetes, oral medications will not help, unlike in T2D treatments. A doctor may prescribe some oral drugs, but their role is just supportive.
Nowadays there are many kinds of insulins, and your doctor may recommend a one that best suits your lifestyle. Long-lasting insulins are useful in a way that there is a need for fewer injections, but short-acting insulins are often better in many conditions.
When taking insulin, the most significant risk is over-dosing and its complications like hypoglycemia (too much drop in the blood glucose), which may be life-threatening. Usually, your doctor or diabetes educator will teach you how to manage such complications.
It is worth knowing that insulin pumps are emerging as much safer and more effective variants in comparison to regular insulin injections. If costs or insurance allows then insulin pumps must be preferred.
Finally, it is essential to know that lifestyle measures are critically important in any type of diabetes. Thus, one needs to learn more about dietary changes and physical activities that can help manage diabetes better. Type 1 diabetes knowledge can make an immense difference in quality of life when living with it. #t1d